Market entry strategies – systematically and efficiently developing new markets
Strategies for successful market entry
Entering new markets and launching new products is an important component of strategic corporate management. However, the success of a go-to-market strategy depends largely on a systematic approach, the necessary market knowledge, and a structured market entry plan. In this overview article, we examine the key factors involved in entering a new market and what companies need to consider when establishing a new product or service.
Regardless of whether you are planning to enter a market with a new product, a new service or into a new national market/abroad – here you will find current tips and know-how for the successful preparation of your market entry.

Where do German companies stand in terms of market entry for new products and services?
According to a recent survey by ZEW Mannheim, the share of revenue generated by German companies through innovations recently hovered at approximately 12% of total revenue. An innovation is defined as a product or service that has been newly introduced or significantly modified in the past three years.
Ten years ago, this share of revenue was still over 15%. Pioneering countries in innovation, such as Switzerland, Sweden, and the USA, regularly show significantly higher figures. This is an alarming development, given that new products and services contribute to meeting rapidly changing customer needs and implementing the latest technology and innovations. For companies that want to succeed in demanding markets and are systematically driving their expansion, go-to-market strategies for market entry with a new product or service play a key role.
What is a go-to-market strategy?
A market entry strategy, according to the usual definition, determines the route a company intends to take to enter a new market. The most common market entry strategies are access to the new market using its own resources (e.g., establishing a separate company), market entry through exports from the existing national subsidiary (often in cooperation with local sales partners or distributors), joint ventures/investments (cooperation with a local company as a means of market entry), or the acquisition of a start-up or established provider to quickly achieve market entry (M&A).
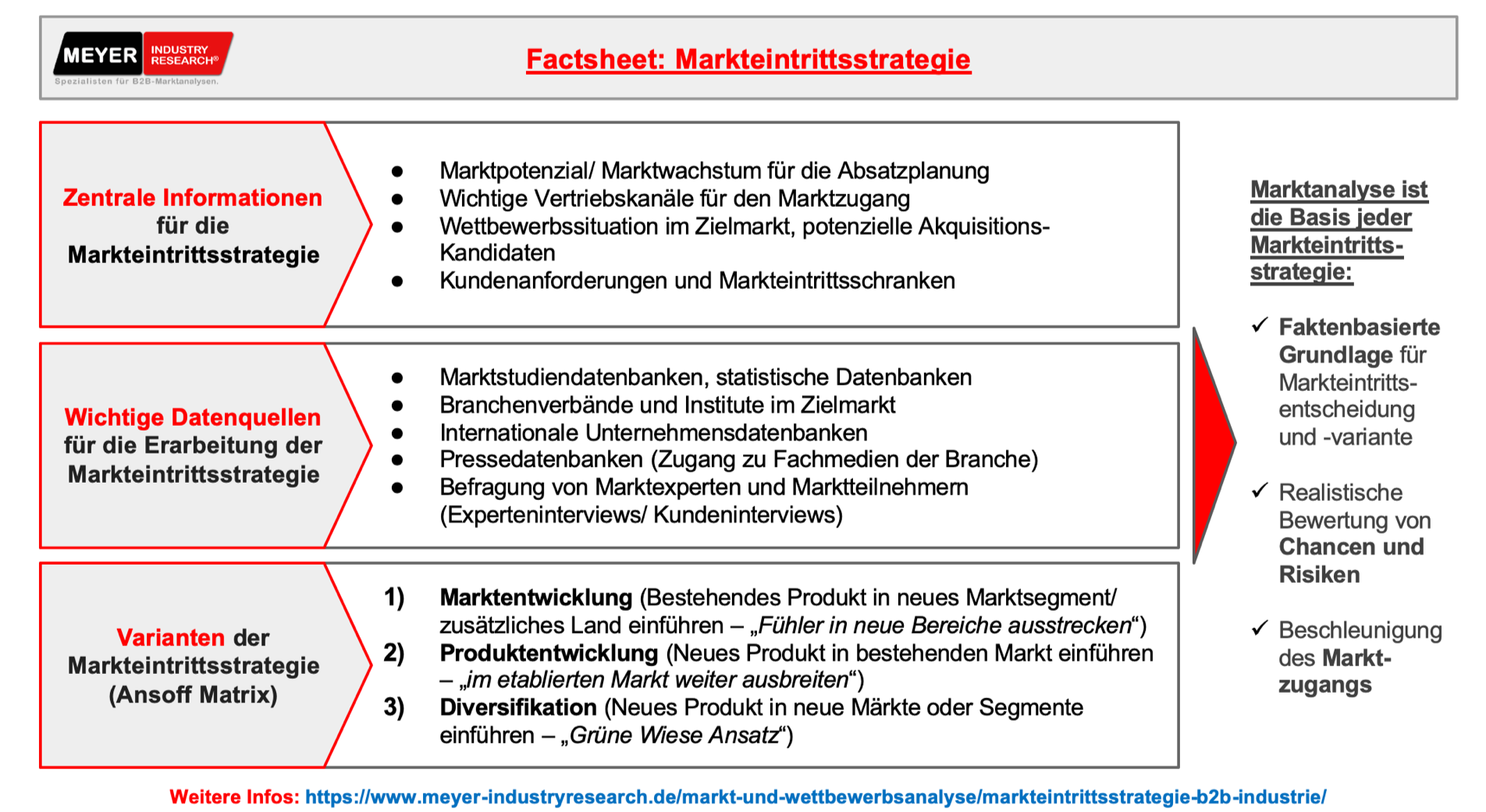
What role does systematic market analysis play in the go-to-market strategy?
market entry analysis is often conducted to determine the appropriate market entry strategy . The market entry analysis serves to provide a reliable assessment of the company's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats for the planned market entry ( SWOT analysis including consideration of market entry barriers be used to identify potential cooperation partners or M&A targets
The foundation of a successful market entry strategy is a thorough investigation of the relevant market using professional market research methods, which can then be used to develop robust strategies and a concrete plan for market entry . The most important market research methods include both secondary research (e.g., statistics, databases, publications from companies in the market, specialist articles) and primary methods (e.g., expert interviews, customer surveys, panels). Many companies also utilize the services of an external market analysis specialist who can assist with expansion into the new market with experience and specialized resources.

What information is needed for a go-to-market strategy?
Every market entry strategy requires a robust preliminary analysis to realistically assess the opportunities and risks in a new market and to facilitate and accelerate entry for the company. A systematic market entry strategy is based on a solid understanding of market potential (market size, market segments, market growth) , the competitive situation (market participants, start-ups, M&A potential) , customer requirements (key target customers/customer groups and their requirements, sales channels) , as well as trends and regulations (e.g., legal requirements, technological trends) in the target market. Based on this information, a reliable decision can be made as to whether developing the market with your own resources, a partnership, or an M&A strategy will provide the most efficient market access. The sub-areas in detail:
1. Market size / market potential
Assessing market potential is a key factor in all market entry strategies. Sales and/or revenue figures for the relevant product or the entire target market are evaluated, usually over the past few years. This also provides initial insights into the company's potential revenue and allows one to assess which investments are sensible given the expected revenue in the market. Typical market size measurements used in market entry strategies include:
- Actual market turnover (e.g. in billion EUR/billion USD)
- Actual number of units sold in the market (depending on the target market, e.g. number of units sold)
- Historical growth of the market (expressed e.g. in the form of a CAGR – Compound Annual Growth Rate)
- Market potential (especially for new markets/products/innovations – theoretically achievable volume in a market)
2. Market growth/ forecast
Market forecasting is also particularly interesting for companies in the context of market entry strategies. This involves assessing how the market is likely to develop in the coming years and how the company can best benefit from this development. Key questions in this context are:
- What growth potential can be expected in the new market in the coming years?
- Which product, technology, and services are growing fastest and are expected to show the best performance in terms of core indicators such as sales, profitability, and market share?
- Which foreign target country offers the most attractive growth potential in the entire market?
3. Market segments
To gain a detailed understanding of the potential, segmenting or subdividing the market is essential for any market entry strategy. Segmentation can be based on various criteria, including:
- Product features/technical segmentation
- Target groups/industries
- Price segments
- regional criteria
Based on the analysis of the market segments, it is possible to assess in which areas entry into the new market is particularly attractive, where resources should be focused in the new market and where marketing and sales should place particular emphasis.
4. Competitive situation
A key aspect of market entry strategies is also the assessment of the competitive situation in the market. Key aspects to consider here include:
- Which competitors are currently active in the market?
- What market share do you have in the target market?
- What financial indicators do competitors achieve in the target market (sales, profit)?
- What strategies does the competition use to operate in the market and what are their strengths and weaknesses?
- Which product segments do you serve under which brand in the target market?
- How is the competition organized (e.g. own organization or joint venture)?
- What measures does the competition use to reach these customer groups?
- What resources do the competitors have and how do they market themselves?
- Which companies (start-ups or established companies) would be interesting for acquisition?
5. Target customers
In addition to analyzing market size and competition, the customer landscape also plays an important role in market entry strategies. Key questions when analyzing target customers include:
- Who are the most important customer companies in the industry?
- How concentrated is the customer landscape (many small providers or a few large companies in the target market, market share of customers?)
- What strategies and skills can be used to develop key accounts?
6. Customer requirements
The term customer requirements encompasses numerous questions that can be addressed within the framework of a market entry strategy:
- What key success factors and requirements must be met to develop the new customer industry/new market?
- Are there barriers to market entry that make market access difficult at home or abroad (e.g. regulatory barriers to market entry such as standards and certificates/approvals or de facto barriers to market entry such as strong customer relationships between suppliers and customer companies)?
7. Sales structure
To be successful in the new market, establishing the right sales strategies plays a key role. Among other things, the following must be clarified:
- What distribution structure is available in the market and is suitable for the best possible placement of the product?
- Which sales partners could be used to implement the market entry, establish the brand in the new market, or expand the business?
- Which companies could be suitable partners, for example through a joint venture, an acquisition or a license agreement?
8. Trends
Finally, the consideration of medium- to long-term trends plays an important role in all types of market entry strategies. This includes, for example, the analysis of the following questions:
- Which trends are driving companies (competitors, customers, suppliers) in the medium to long term and should therefore be taken into account for a successful market entry?
- Are there innovative start-up companies in the area that are advancing new technologies and thus changing the landscape?
- Could disruptive technologies or substitutes fundamentally change the market or the companies in the industry, and what strategies could be used to counter this?
Based on this information, market entry strategies can be developed reliably and market entry can be successfully implemented.

How much does it cost to develop robust market entry strategies?
If specialized external service providers are commissioned to develop market entry strategies, the cost issue should be discussed as precisely as possible in advance. Reputable agencies will provide a binding, fixed-price quote for market entry strategies in advance and often also offer to divide the project into clear sub-steps. The costs for developing a robust market entry strategy depend on the target market being examined (definition of market, product, service), the regional scope of the study (Germany, Europe, world), and the required detailed information. Typical budgets range between €10,000 and €50,000, and approximately 6-12 weeks should be planned for careful implementation.

Any questions? We're happy to support you with your market entry!
As a professional consulting firm for market entry strategies, MEYER INDUSTRY RESEARCH is your reliable partner for acquiring important market, customer, and competitor information in a new market. We support you in your market entry with structured market research and, in close collaboration with you, derive a systematic plan and strategies for the implementation of successful market entry strategies. With our resources and experience, you can lead your market entry or expansion into a new market to success.
We have particular experience in market entry strategies in the industrial and B2B sectors. Our market entry consulting firm's clients include medium-sized and large companies in the automotive, mechanical and plant engineering, medical technology, and energy technology sectors. We also regularly work for international companies that want to develop their products in a structured way into the German or European market and utilize our market entry expertise for this purpose.
contact

Leave a comment